KodeKloud CKS Challenge 04
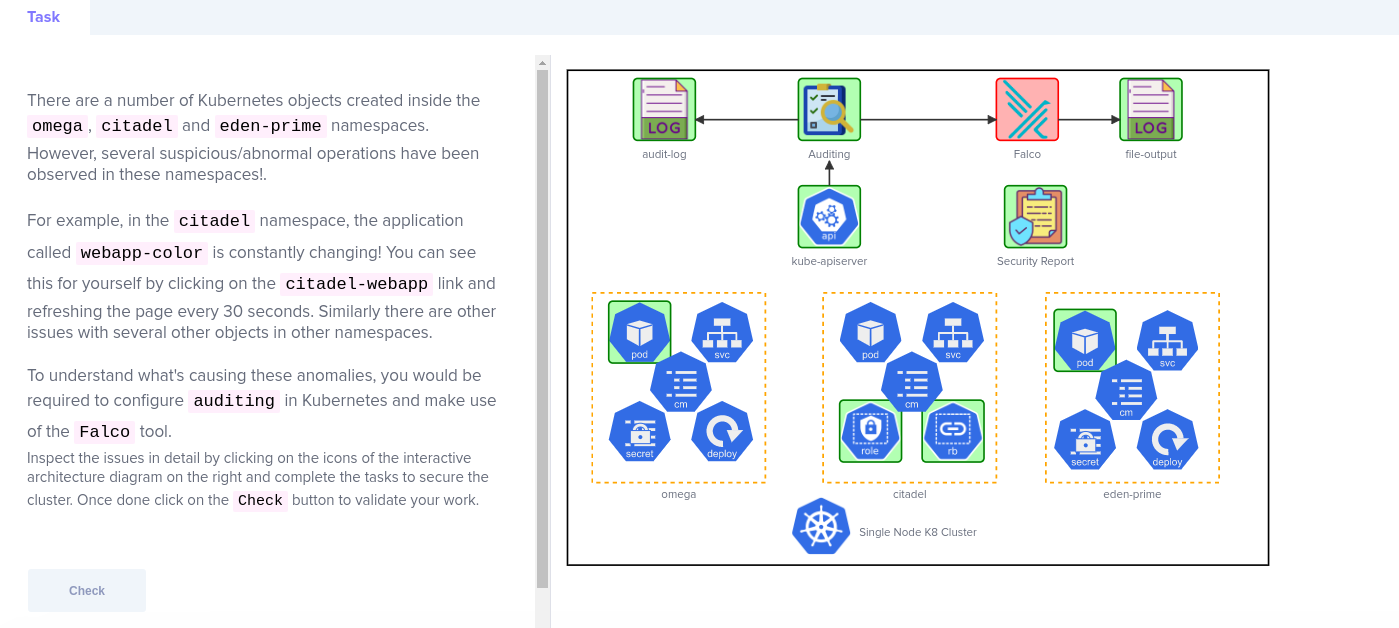
This challenge focused on how to analysis/audit suspicious behaviors using, using Falco and Kubernetes auditing.
Please note that the grading system has not picked the installed version of Falco, hence the Task is marked as incomplete.
According to the Falco documentations, there have been recent change to the systemd unit names. See here.
Install and configure Falco
Falco is a software tool that monitors and alerts on activities that involve making system calls in a Linux operating system. It uses a combination of user space and kernel space modules to monitor and analyze the system calls made by processes on the system.
Falco is capable of identifying specific system calls, arguments, and properties of the calling process, and uses a rules engine to filter and alert on suspicious events. When such events are detected, Falco can be configured to notify various outputs, such as Syslog, files, or Standard Output, so that security teams or system administrators can investigate and take appropriate action.
The installation is straightforward, here I have used Kmod as the preferred plugin to install.
Installation
Following installation steps are directly copied from the official Falco documentation, it is recommended to refer to the documentation, if you wish to install Falco in your system.
# Trust the falcosecurity GPG key
curl -fsSL https://falco.org/repo/falcosecurity-packages.asc | \
sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/falco-archive-keyring.gpg
# Configure the apt repository
sudo cat >>/etc/apt/sources.list.d/falcosecurity.list <<EOF
deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/falco-archive-keyring.gpg] https://download.falco.org/packages/deb stable main
EOF
# Update the package list
sudo apt-get update -y
# Install some required dependencies that are needed to build the kernel module and the BPF probe
sudo apt install -y dkms make linux-headers-$(uname -r)
# If you use the falco-driver-loader to build the BPF probe locally you need also clang toolchain
sudo apt install -y clang llvm
# You can install also the dialog package if you want it
sudo apt install -y dialog
# Install the Falco package
sudo apt-get install -y falco
The driver, I have associated in this scenario is kmod, and I have enabled the automatic rule-sets update.
See here for the complete installation guide.
Once installed, we can list Falco systemd services as below

Once it is verified that Falco is running, we might need to update it to log the events in /opt/falco.log.
Following config needs to be updated in /etc/falco/falco.yaml
file_output:
enabled: true
keep_alive: false
filename: /opt/falco.log
Once done, we can restart the falco service,
systemctl restart falco
To verify if Falco is writing the logs under /opt/falgo.log,
root@controlplane ~ ➜ tail /opt/falco.log
04:50:46.879494591: Error Package management process launched in container (user=root user_loginuid=-1 # REDACTED
04:51:02.150123544: Error Package management process launched in container (user=root user_loginuid=-1 # REDACTED
04:51:27.142434942: Error Package management process launched in container (user=root user_loginuid=-1 # REDACTED
04:51:47.137437708: Error Package management process launched in container (user=root user_loginuid=-1 # REDACTED
Configure Kubernetes Auditing
Though the following statement is a bit vague to me when I was read it for the first time, we can get the gist of it.
Create a single rule in the audit policy that will record events for the ‘two’ objects depicting abnormal behaviour in the ‘citadel’ namespace. This rule should however be applied to all ‘three’ namespaces shown in the diagram at a ‘metadata’ level. Omit the ‘RequestReceived’ stage.
So if we refer to the objects in citadel namespace, it is clear that,
configmapwebapp-config-mappodwebapp-color
are keep replacing. So the two object types that mention above are configmaps and pods.
Secondly, the audit rule should only focus on omega, citadel and eden-prime namespaces in metadata level.
See below auditing policy.
# /etc/kubernetes/audit-policy.yaml
apiVersion: audit.k8s.io/v1 # This is required.
kind: Policy
omitStages:
- "RequestReceived"
rules:
- level: Metadata
resources:
- group: ""
# Resource "pods" doesn't match requests to any subresource of pods,
# which is consistent with the RBAC policy.
resources: ["pods", "configmaps"]
namespaces: ["omega", "citadel", "eden-prime"]
Before we started to change the API server configuration, lets provision a directory for the Audit logs.
mkdir -p /var/log/kubernetes/audit/
Kube API Server configuration
Update the following configuration in the kube-apiserver manifest file in /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-apiserver.yaml
First, lets configure the volumes and volume mounts
Then we can update kube-apiserver arguments enable auditing.
Below manifest file only highlights the intended configurations
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
# REDACTED
name: kube-apiserver
namespace: kube-system
spec:
containers:
- command:
- kube-apiserver
- --audit-policy-file=/etc/kubernetes/audit-policy.yaml
- --audit-log-path=/var/log/kubernetes/audit/audit.log
# REDACTED
name: kube-apiserver
volumeMounts:
# REDACTED
- mountPath: /etc/kubernetes/audit-policy.yaml
name: audit
readOnly: true
- mountPath: /var/log/kubernetes/audit/
name: audit-log
readOnly: false
# REDACTED
volumes:
- name: audit
hostPath:
path: /etc/kubernetes/audit-policy.yaml
type: File
- name: audit-log
hostPath:
path: /var/log/kubernetes/audit/
type: DirectoryOrCreate
# REDACTED
status: {}
Monitoring
As both the Kubernetes auditing and Falco monitoring has been set up, we can investigate the suspicious behaviours.
Kubernetes Audit logs
Here is a sample of the audit log,
tail /var/log/kubernetes/audit/audit.log | jq
{
"kind": "Event",
"apiVersion": "audit.k8s.io/v1",
"level": "Metadata",
"auditID": "c59aa70d-a830-4c23-9d67-0f37844a4cfc",
"stage": "ResponseComplete",
"requestURI": "/api/v1/namespaces/citadel/pods?fieldManager=kubectl-create",
"verb": "create",
"user": {
"username": "kubernetes-admin",
"groups": [
"system:masters",
"system:authenticated"
]
},
"impersonatedUser": {
"username": "agent-smith",
"groups": [
"system:authenticated"
]
},
"sourceIPs": [
"192.168.121.1"
],
"userAgent": "kubectl/v1.20.0 (linux/amd64) kubernetes/af46c47",
"objectRef": {
"resource": "pods",
"namespace": "citadel",
"name": "webapp-color",
"apiVersion": "v1"
},
"responseStatus": {
"metadata": {},
"code": 201
},
"requestReceivedTimestamp": "2023-05-14T04:43:42.223786Z",
"stageTimestamp": "2023-05-14T04:43:42.229044Z",
"annotations": {
"authorization.k8s.io/decision": "allow",
"authorization.k8s.io/reason": "RBAC: allowed by RoleBinding \"important_binding_do_not_delete/citadel\" of Role \"important_role_do_not_delete\" to User \"agent-smith\"",
"pod-security.kubernetes.io/enforce-policy": "privileged:latest"
}
}
The first clue to solve this (at least to me) was above recurring event, which explain why the webapp-color pod keep changing.
So the culprit is agent-smith, lets delete both the role and role-binding, which allow this user to perform this.
# To get the role and role-binding
root@controlplane ~ ➜ kubectl get rolebindings.rbac.authorization.k8s.io -o wide -n citadel
NAME ROLE AGE USERS GROUPS SERVICEACCOUNTS
dev1 Role/dev1 50m dev-user
important_binding_do_not_delete Role/important_role_do_not_delete 50m agent-smith
important_citadel_user_binding Role/important_citadel_user_role 50m citadel-user
# Delete the role
kubectl delete role important_role_do_not_delete -n citadel
# Delete the role-binding
kubectl delete rolebindings.rbac.authorization.k8s.io important_binding_do_not_delete -n citadel
Falco events
Let’s investigate Falco events in /opt/falco.logs
root@controlplane ~ ➜ tail /opt/falco.log
04:50:46.879494591: Error Package management process launched in container (user=root user_loginuid=-1 command=apt install nginx pid=27616 container_id=8bfd921f6a90 container_name=k8s_eden-software2_eden-software2_eden-prime_c62cd7c1-37c2-47cc-88d6-cbf4434f480b_0 image=ubuntu:latest)
04:51:02.150123544: Error Package management process launched in container (user=root user_loginuid=-1 command=apt install nginx pid=27799 container_id=8bfd921f6a90 container_name=k8s_eden-software2_eden-software2_eden-prime_c62cd7c1-37c2-47cc-88d6-cbf4434f480b_0 image=ubuntu:latest)
04:51:27.142434942: Error Package management process launched in container (user=root user_loginuid=-1 command=apt install nginx pid=28557 container_id=8bfd921f6a90 container_name=k8s_eden-software2_eden-software2_eden-prime_c62cd7c1-37c2-47cc-88d6-cbf4434f480b_0 image=ubuntu:latest)
04:51:47.137437708: Error Package management process launched in container (user=root user_loginuid=-1 command=apt install nginx pid=29039 container_id=8bfd921f6a90 container_name=k8s_eden-software2_eden-software2_eden-prime_c62cd7c1-37c2-47cc-88d6-cbf4434f480b_0 image=ubuntu:latest)
04:52:01.398472097: Error Package management process launched in container (user=root user_loginuid=-1 command=apt install nginx pid=29254 container_id=8bfd921f6a90 container_name=k8s_eden-software2_eden-software2_eden-prime_c62cd7c1-37c2-47cc-88d6-cbf4434f480b_0 image=ubuntu:latest)
04:52:26.403328190: Error Package management process launched in container (user=root user_loginuid=-1 command=apt install nginx pid=30042 container_id=8bfd921f6a90 container_name=k8s_eden-software2_eden-software2_eden-prime_c62cd7c1-37c2-47cc-88d6-cbf4434f480b_0 image=ubuntu:latest)
04:52:46.383109164: Error Package management process launched in container (user=root user_loginuid=-1 command=apt install nginx pid=30503 container_id=8bfd921f6a90 container_name=k8s_eden-software2_eden-software2_eden-prime_c62cd7c1-37c2-47cc-88d6-cbf4434f480b_0 image=ubuntu:latest)
04:53:01.663770736: Error Package management process launched in container (user=root user_loginuid=-1 command=apt install nginx pid=30696 container_id=8bfd921f6a90 container_name=k8s_eden-software2_eden-software2_eden-prime_c62cd7c1-37c2-47cc-88d6-cbf4434f480b_0 image=ubuntu:latest)
04:53:26.675809498: Error Package management process launched in container (user=root user_loginuid=-1 command=apt install nginx pid=31525 container_id=8bfd921f6a90 container_name=k8s_eden-software2_eden-software2_eden-prime_c62cd7c1-37c2-47cc-88d6-cbf4434f480b_0 image=ubuntu:latest)
04:53:46.659625483: Error Package management process launched in container (user=root user_loginuid=-1 command=apt install nginx pid=32016 container_id=8bfd921f6a90 container_name=k8s_eden-software2_eden-software2_eden-prime_c62cd7c1-37c2-47cc-88d6-cbf4434f480b_0 image=ubuntu:latest)
Here, the culprit is a container belongs to a pod in eden-prime namespace, so we have to terminate the pods.
The container name, according to the above logs is container_name=k8s_eden-software2_eden-software2
To terminate the specific pod
kubectl delete pod eden-software2 -n eden-prime
Additional tasks
To finalise the task, lets dump the objects that are suspicious as requested by the task.
# Roles and RoleBinding
echo "agent-smith,important_role_do_not_delete,important_binding_do_not_delete" > /opt/blacklist_users
# Pods
echo "eden-prime,eden-software2" > /opt/compromised_pods